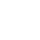Exploring the Obstacles and Benefits of Various Ethernet Cable Categories
Often defined as the "plumbing pipes of the Internet", Ethernet encompasses an entire range of twisted pair and fiber cables that are constantly being upgraded and standardized by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). Each new category of Ethernet improves upon noise cancelation and supports increasingly faster bandwidth speeds.
Different Twisted Pair Ethernet Categories
| CAT5 | CAT5e | CAT6 | CAT6e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Data Transmission Speed (Mbit/s) | 100 Mbps (100BASE-TX) | 1 000 Mbps (with 1000BASE-T) 2 500 Mbps (with 2.5GBASE-T) 5 000 Mbps (with 5GBASE-T) ** | 5 000 Mbps (with 5GBASE-T) 10 000 Mbps (with 10GBASE-T)** | 10 000 Mbps (with 10GBASE-T) |
Cable rating (Mhz) | 100 MHz | 100 MHz | 250 MHz | 500 MHz |
** At shorter cable length, it is possible to use cables of a lower grade than what is required for 100 m. For example, it is possible to use 10GBASE-T on a CAT6 cable of 55 m or less. Likewise, 5GBASE-T is expected to work with Cat5e in most use cases up to 55 m.
Do you know why copper pairs are twisted?
Source: Demystifying Ethernet Types
Unveiling the Wonders of CAT5e: Why we should all like it ?
- CABLES : With more than 70 billion meters of CAT5e cables deployed today across the world, we do not want to open every wall to replace the cables. Assuming it is even possible, … cost estimates to remove cat5e can scale to unreasonable budgets per building.
- INTERFACES : Most of the devices having an Ethernet port always supports CAT5e, laptop, switchers, PC, ...
- COST : CAT5e is still the most common type of cabling used for deployments due to its ability to support Gigabit speeds at a cost-effective price. Therefore, we have to find a solution to move on with these cables whatever the video resolutions.
- intoPIX innovations : Compression is a MUST if we don't want to change all the existing infrastructure. Great news, intoPIX has developed unique video compression solutions preserving pristine quality and offering extremely low latency. Exactly what is needed for you to leverage existing CAT5e IP infrastructures. Ever heard about TicoXS and TicoXS FIP?
"The lightweight low-power intoPIX TicoXS and TicoXS FIP including JPEG XS & Flawless Imaging profile are the ideal solutions to distribute true 4K60 444 and 8K30P or 60P over standard CAT5e cables & switchers, while preserving low latency & high quality with super-low complexity and cost"
Embark on your AV journey with intoPIX & CAT5e: From HD to 4K to 8K
Embark on your AV journey with intoPIX & CAT5e: From HD to 4K to 8K
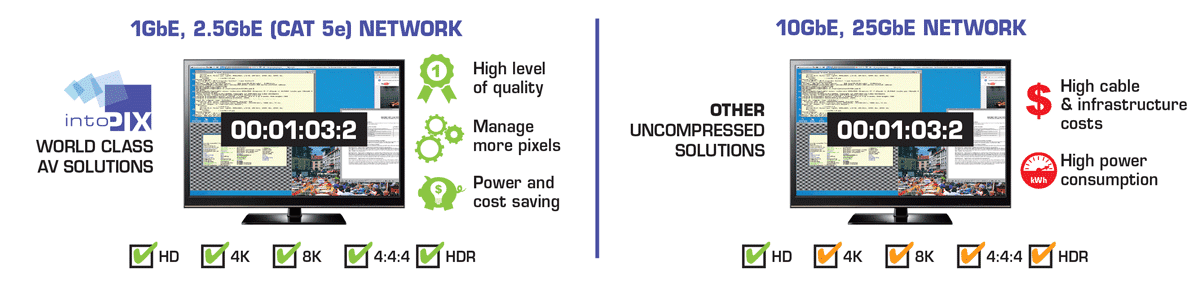
The lightweight low-power TicoXS FPGA cores and FastTicoXS SDKs software implementations allow preserving low latency & high quality with super-low complexity: it offers upgrade capability to new formats (4K/8K) on existing cables (CAT5e). Interoperability can even be guaranteed thanks to the use of open ST2110 & JPEG XS standards.
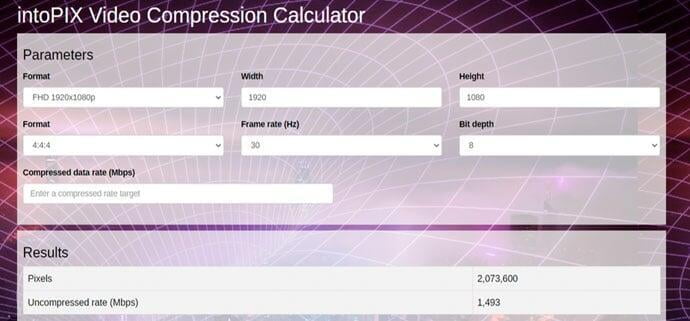
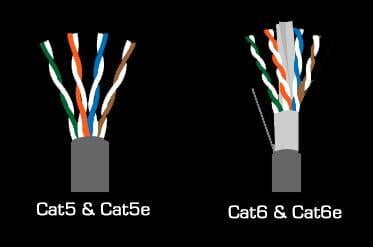
Uncompressed is not an option anymore !
intoPIX compression technology helps to manage more pixels over a limited bandwidth using existing devices and infrastructures. The TicoXS including JPEG XS & Flawless Imaging profile (FIP) technology helps you to manage higher resolutions, frame rates and number of streams, while keeping the uncompressed visual quality with no latency and a very low hardware/software complexity. In addition to power consumption savings, intoPIX compression reduces BOM cost thanks to cheaper switches, less cabling, smaller FPGAs and a better use of CPU/GPU processing power.